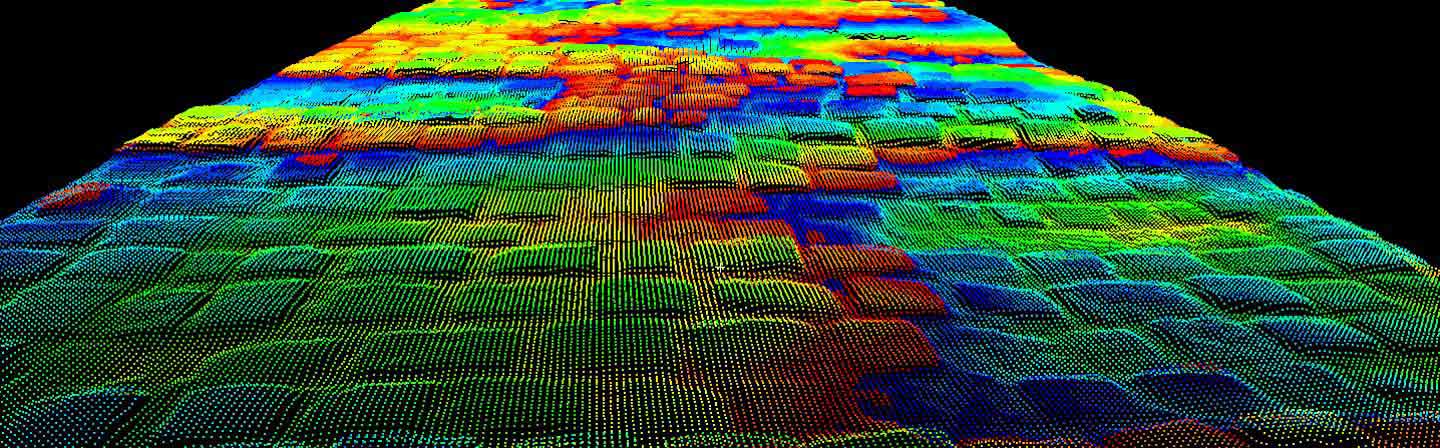
The 3D and 2D geometry of an object can be used to obtain detailed information on its shape and state. Comparing the geometry and state of an object across multiple field measurements provides information about the long-term change dynamics: For example, when cobblestones are damaged, they slowly begin to subside. Depending on the extent of the subsidence, the road may need to be improved or even completely rebuilt. This type of information can be obtained through a skilled evaluation of geometric data.
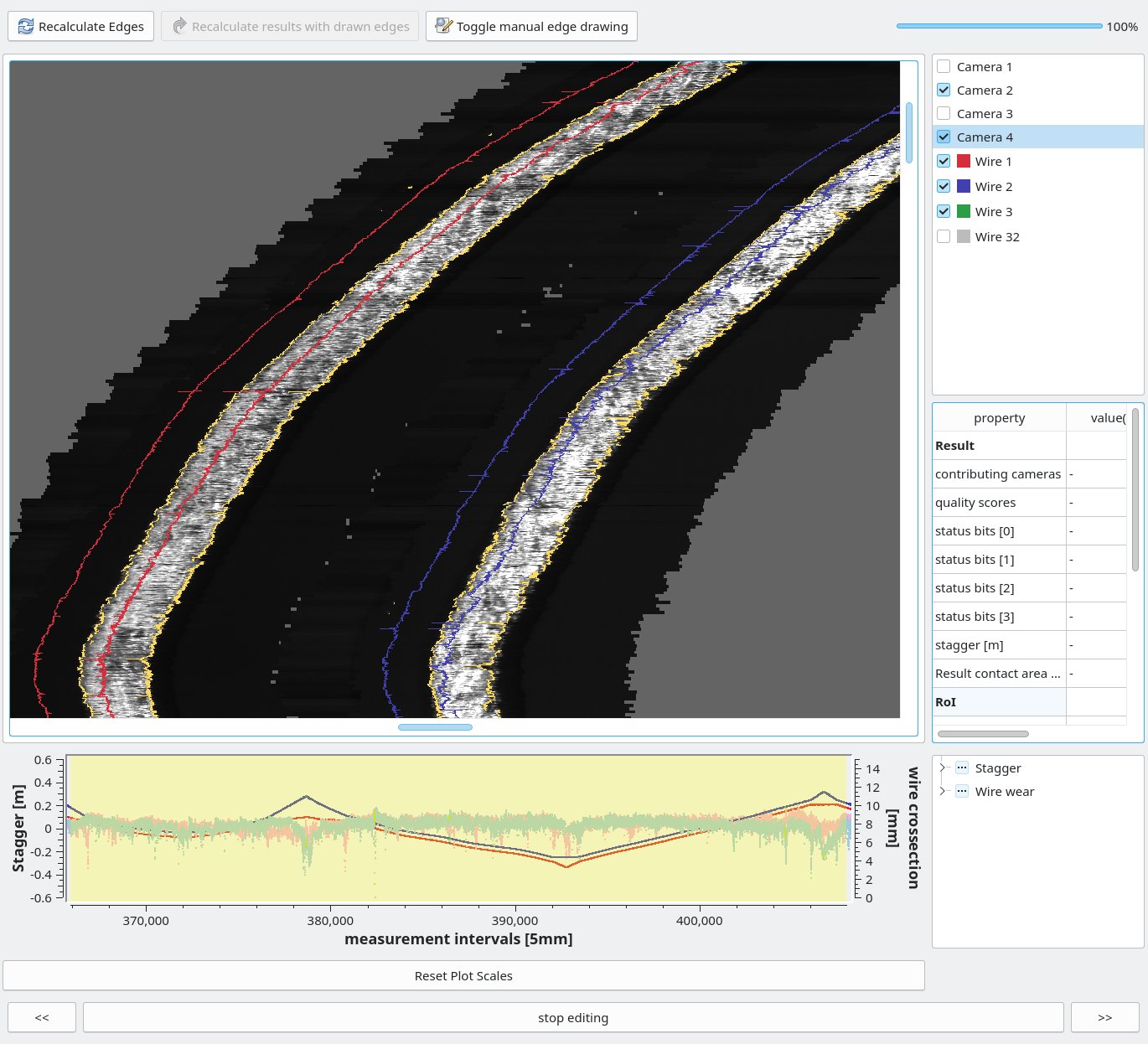
We use custom algorithms and neural networks for edge detection and target-performance comparison directly in the 3D model to analyze the measurement data. This method can be used for the regular inspection and automatic assessment of the condition of transportation infrastructure such as railroads, including their many individual objects – poles, train platforms, overhead wires, etc. This enables predictive maintenance.
Fusing 2D and 3D data for high-resolution crack detection
When inspecting buildings, subtle structures such as cracks need to be reliably detected and measured. We use a combination of 2D and 3D data for crack detection. Neural networks form the basis for our high-resolution damage detection, even in complex surroundings such as bridges, canals or shafts. Methods based on photogrammetry and LiDAR help to accurately determine the deviations and geometric changes in 3D over long inspection intervals.
Other types of surface damage such as spall, exposed reinforcements or repaired damaged areas can also be detected using the image data. We also use passive thermography to detect delamination and spall.