Detection of trace gases and detection of residual absorbtion
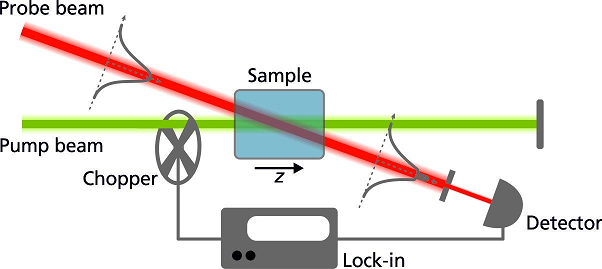
Highly sensitive laser-based spectroscopy methods are primarily used for analytical tasks when it comes to detecting low trace gas concentrations or residual absorption in optical materials. Photothermal common-path interferometry (PCI) uses the secondary effect of the refractive index change resulting from the absorption-induced heating of a material. The absorbed radiation of a powerful pump laser in the material produces a change in the refractive index (»thermal lens«). A second, weak probe laser crosses the beam of the pump laser. The thermal lens causes a modification in the wavefront of the probe laser. Using a lock-in method, this can be measured very sensitively and the strength of the absorption can be determined.