Time-of-flight measurement (LiDAR): Method of choice
Various methods such as photogrammetry, triangulation, holography or time-of-flight measurements have become established for the optical 3D measurement of objects in space.
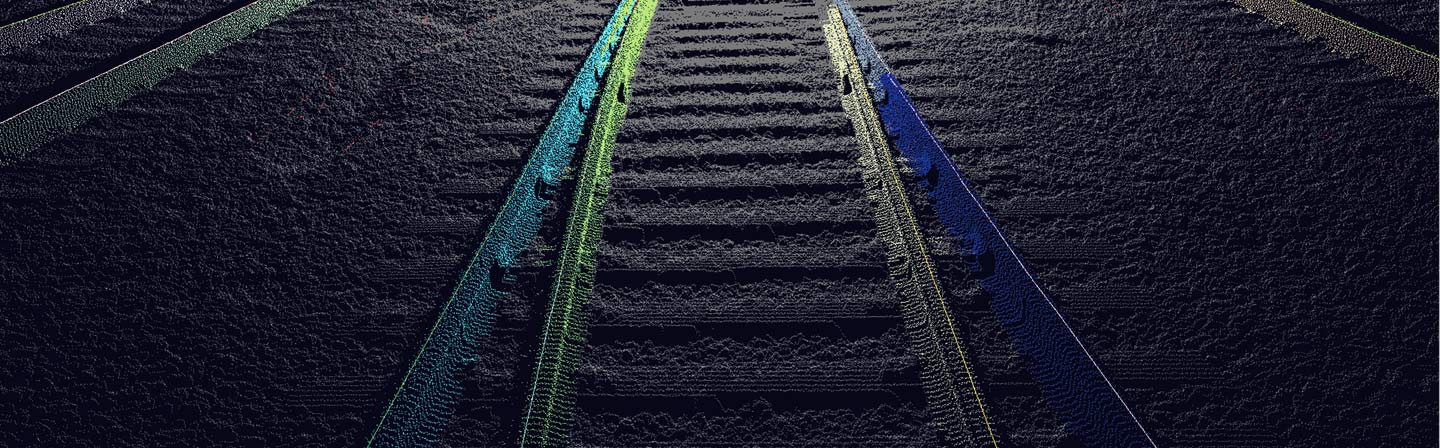
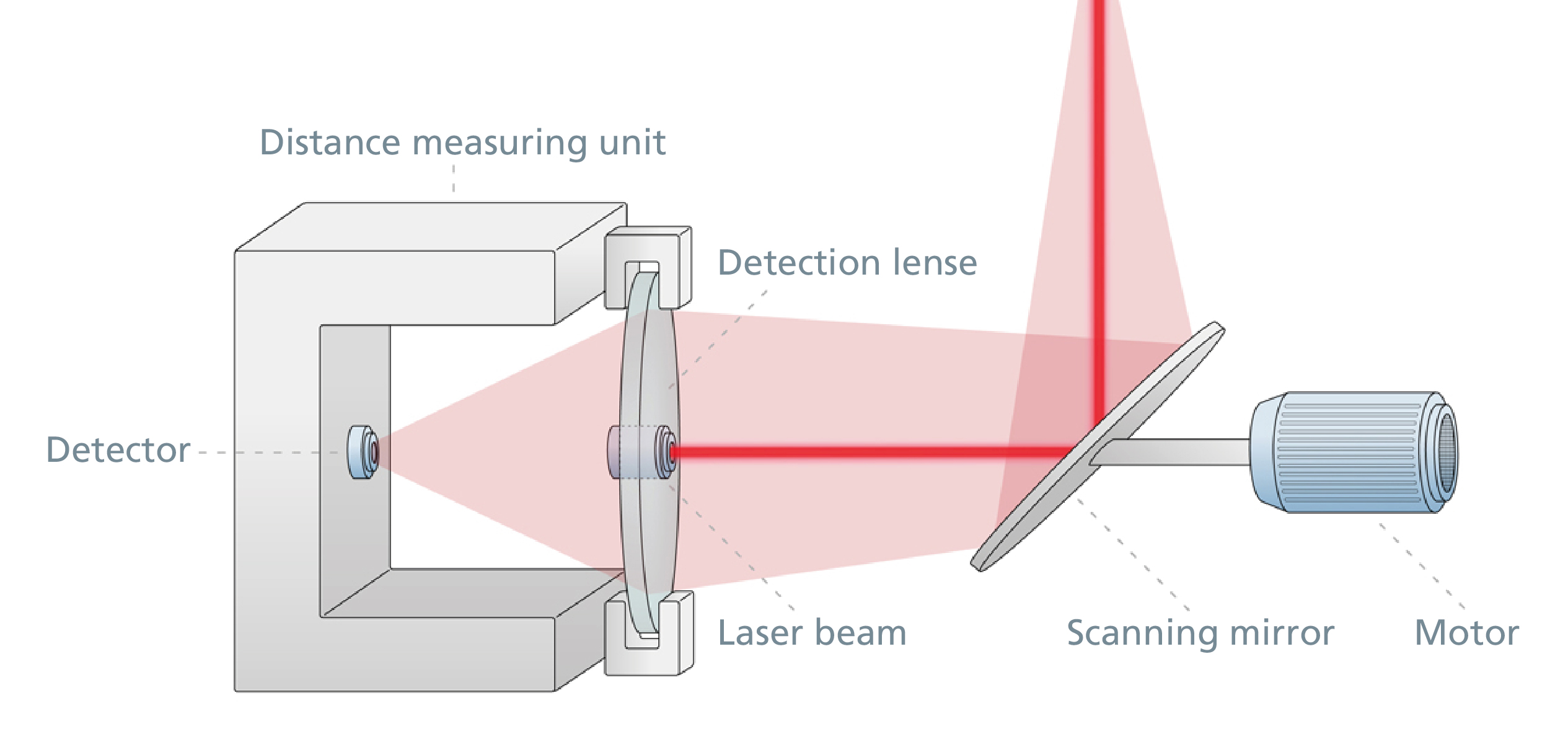
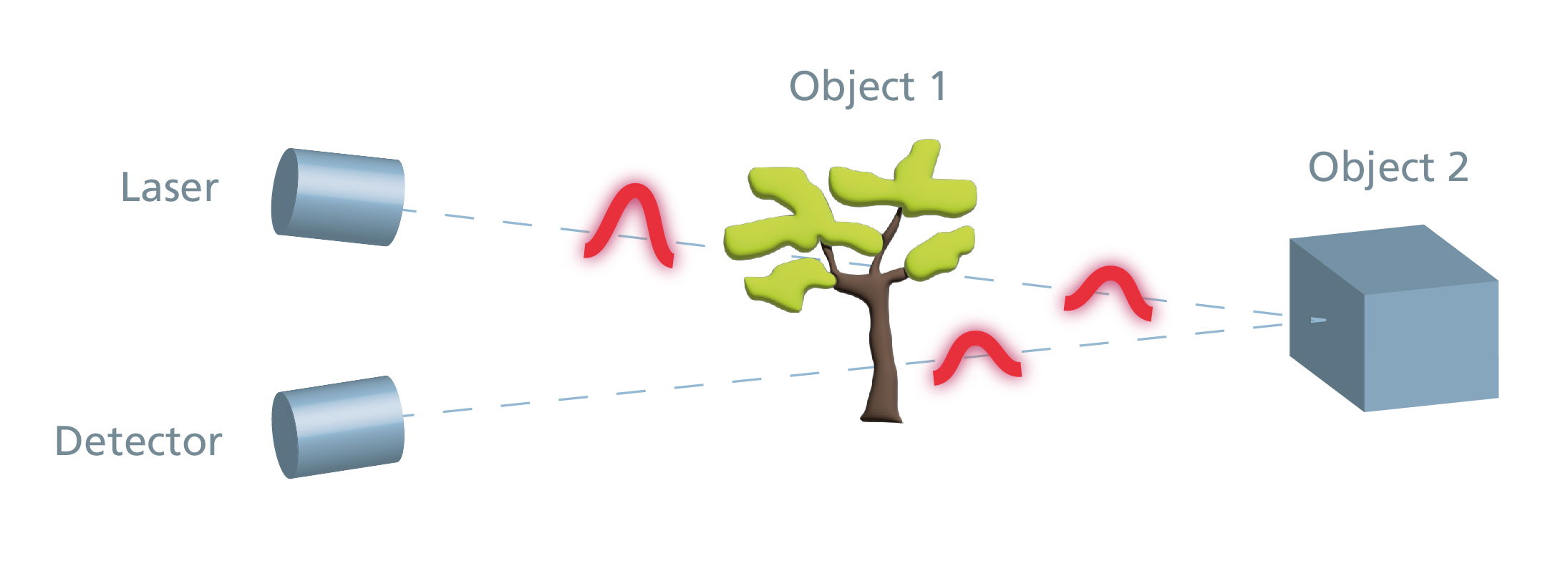
The distance measurement by means of time-of-flight measurement of laser light (LiDAR, light detection and ranging) is the method we use most frequently. In the range of a few centimeters up to several hundred meters it is the method of choice when high accuracy and measuring speed have to be achieved even under difficult and changing environmental conditions. To measure distances, light is emitted and reflected by the object. The distance between the measuring device and the target object can be determined on the basis of the speed of light and the measured time-of-flight of the light from the light source (emitter) to the object and back to the detector.
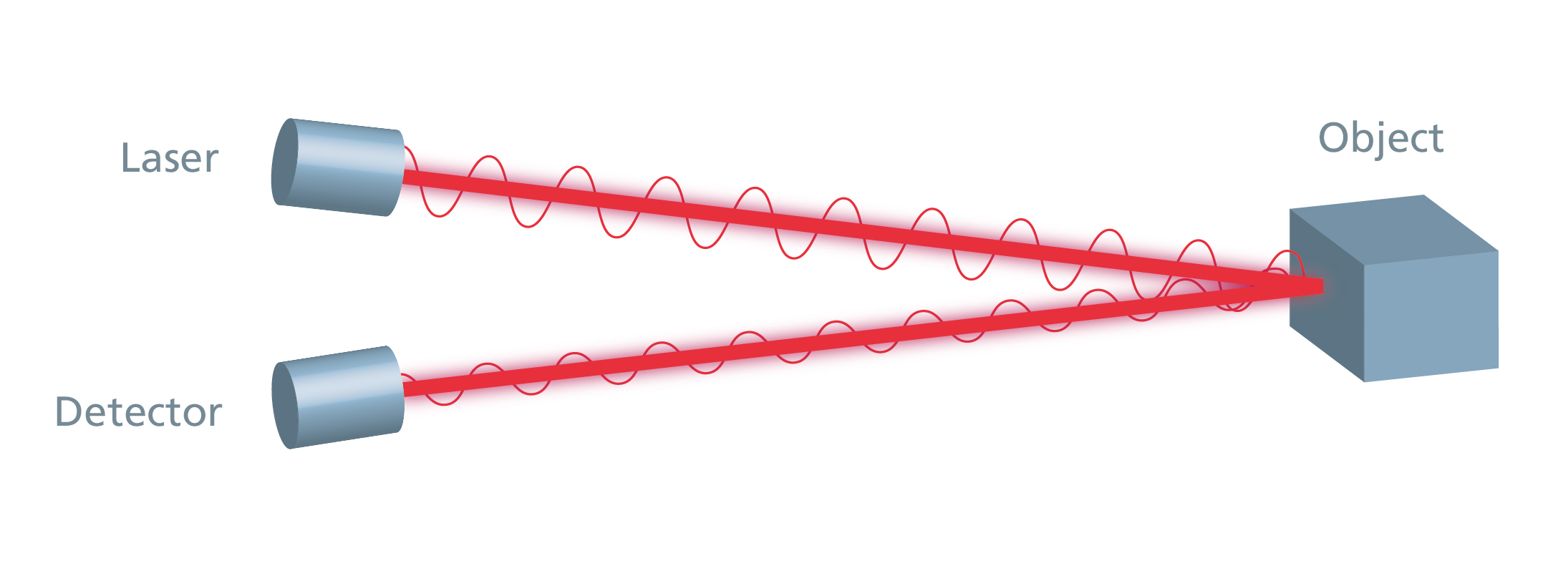
The light, in our case always laser light, is modulated in its intensity. We use both pulsed time-of-flight and phase shift measurement methods, which complement each other well in their strengths and weaknesses.